Psychiatric assistance dogs often unavailable to young people
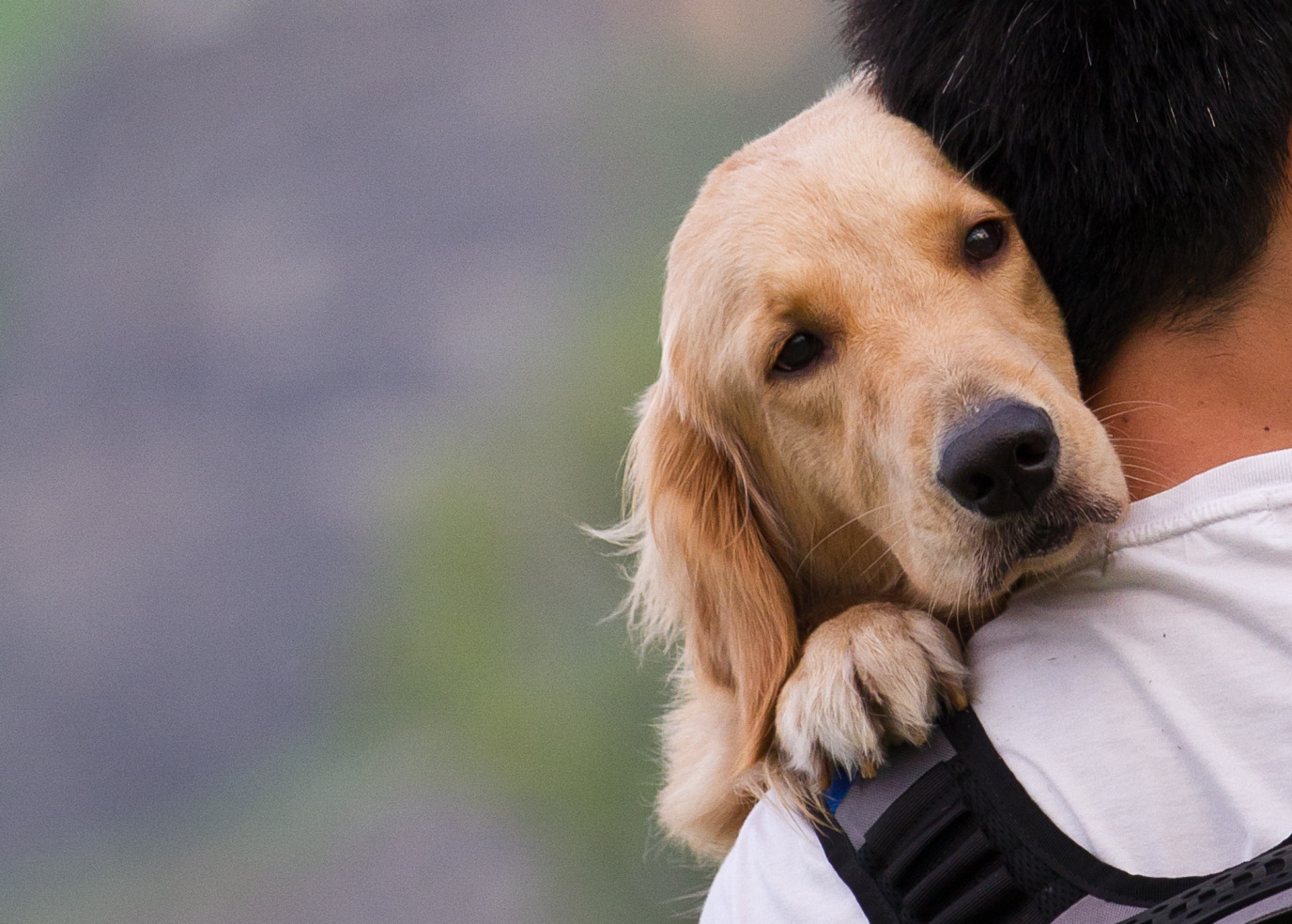

Young people with severe psychological issues often face bureaucratic hurdles and high costs that prevent them from obtaining a psychiatric assistance dog, despite these dogs having the potential to significantly improve their quality of life. This is the conclusion of a study conducted by a group of young experts by experience in collaboration with the University of Groningen.
A psychiatric assistance dog helps young people detect stress and nightmares and, according to the study, can greatly improve their quality of life. This is especially true for those who have been with their dog for more than two years. Many young people reported that their assistance dog is the main reason they are still here.
Inequality
Since these dogs must master a wide range of specific skills, officially trained assistance dogs are expensive. However, there is no national compensation, meaning many young people rely on local municipal schemes through the Social Support Act (Wmo). The rules for this vary greatly by municipality, leading to much frustration and inequality.
Health insurance
Unlike assistance dogs for the blind, deaf, and people with physical disabilities, psychiatric assistance dogs are not covered by health insurance in the Netherlands. This is despite the fact that insurers participating in the study indicated that psychiatric assistance dogs could potentially save healthcare costs in the long run. Young people who try to fund their dog through crowdfunding often face negative reactions and must expose their vulnerabilities online.
Unique collaboration
What is remarkable about the study is the close collaboration between young people and scientists, made possible by a special grant from ZonMw. Young experts by experience were co-researchers, providing a unique and valuable contribution. Their personal experiences gave deeper insight into the issues they and others face. The collaboration not only resulted in scientific findings but also practical recommendations from various interviewed groups. The team hopes for a follow-up grant to continue the research.
The research team consisted of experts by experience Robin, Gunou, Mylèn, and Alynda, and researchers Steffie van der Steen (University of Groningen) and Annemiek Harder (Erasmus University Rotterdam).
More information
- Project website with all research findings
- Profile page Steffie van der Steen
- Scientists and youth collaborate to improve the application process for psychosocial service dogs
| Last modified: | 19 September 2024 2.34 p.m. |
More news
-
17 December 2024
Autism in women: masking takes its toll
Women with autism are often diagnosed later than men. Researcher Yvonne Groen developed a screening tool together with her colleagues to simplify the diagnosis.
-
26 November 2024
The fear of eating
Renate Neimeijer conducts research into eating disorders among children and young adults. Her current research focuses on ARFID: avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder.
-
05 November 2024
Do parents have any influence on whether their children wear 'pink' or 'grey' glasses?
How does a positive outlook actually develop? How important is upbringing in this regard? And what kind of role does optimism actually play in the daily lives of parents and children? Charlotte Vrijen is trying to find an answer to these questions....