The missing link to make easy protein sequencing possible?
There has been a real race among scientists to create a technology that enables easy protein sequencing. Professor of Chemical Biology Giovanni Maglia of the University of Groningen has now found the missing piece in the puzzle: a way to transport a protein through a nanopore, which allows sequencing of proteins in a simple, handheld device.
Science Newsroom | Charlotte Vlek
DNA sequencing has been a revolution in how we understand life, and sequencing proteins is the next holy grail. Maglia explains: ‘DNA is mostly static. The processes in our cells are executed by proteins: they do the actual work. And by understanding proteins, we will understand even more about how our bodies work.’
Why would we want to sequence proteins?
The problem of pulling proteins through a hole
There are currently handheld devices on the market that can sequence DNA. These devices use nanopore technology: a single strand of DNA is pulled through a tiny hole (a nanopore) in a membrane, and as they pass through, the sequence of building blocks in the DNA strand can be ‘read’.
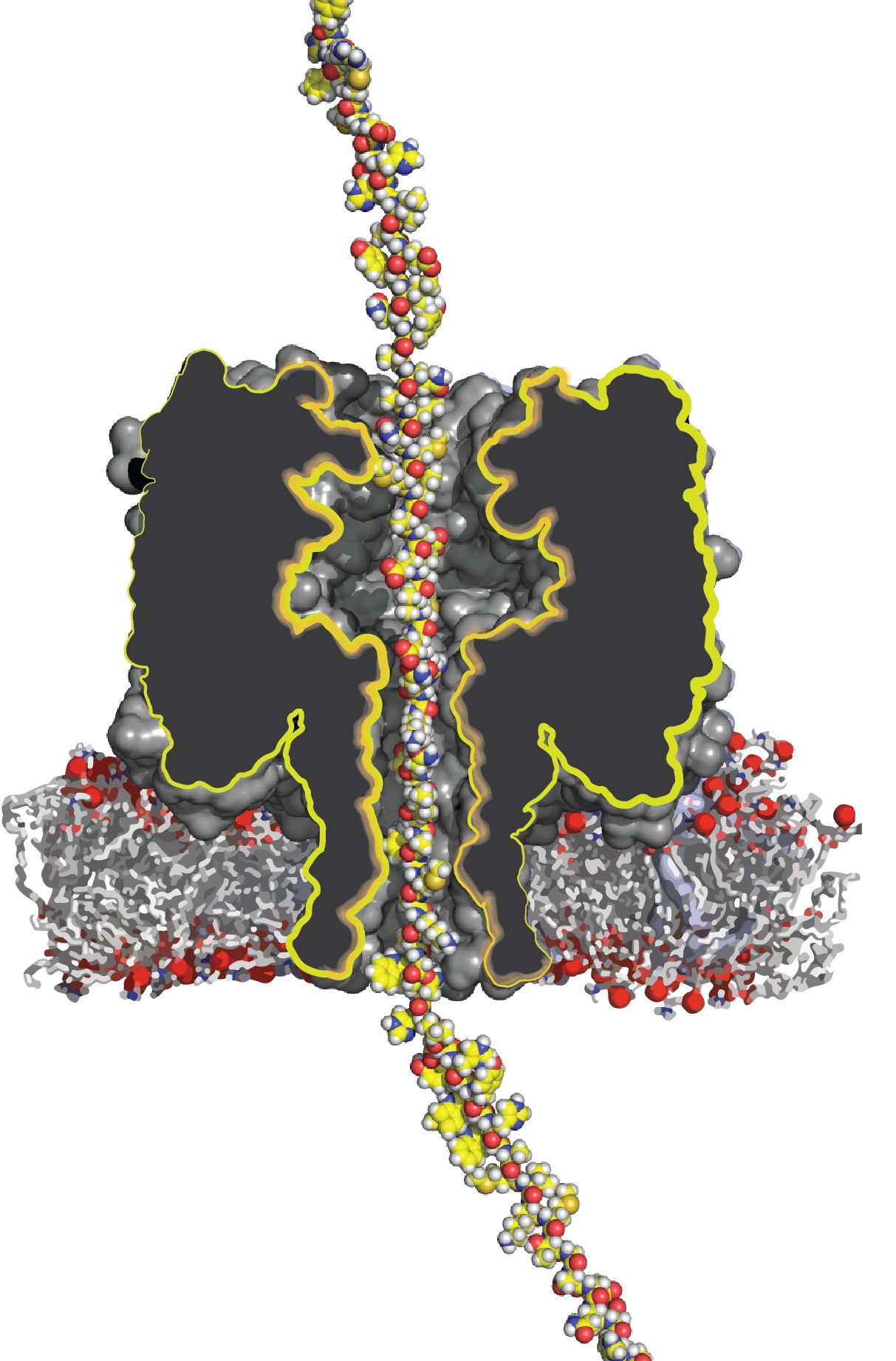
There have been steps towards applying the same nanopore technology to proteins, but it was not yet possible to transport a long protein through the tiny hole in the same way as a DNA strand. ‘It’s like cooked spaghetti,’ Maglia explains. ‘These long strands want to be disorganized, they do not want to be pushed through this tiny hole.’
Single-stranded DNA is also a bit like cooked spaghetti, but it can be pulled through with an electric field because DNA itself is electrically charged. But proteins have a weaker charge, and can carry either positive or negative charge. ‘Proteins and DNA are different,’ Maglia explains, ‘so the technology needs to be adapted.’
Going with the flow
To transport a protein through a nanopore, Maglia used a solution of electrically charged particles (ions), which can be pulled through the nanopore with an electric field. When this happens, they drag along the protein. It was not at all trivial to make this work, Maglia explains: ‘we didn’t know whether the flow would be strong enough. Furthermore, these ions want to move both ways, but by attaching a lot of charge on the nanopore itself, we were able to make it directional.’
Maglia engineered a system with the strongest possible flow without proteins. In a collaboration with researchers of the University of Rome Tor Vergata, computer simulations were performed, that revealed that the force of this flow on a protein was comparable to the force of the electric field on DNA. Maglia then tried it on a difficult protein: one with many negative charges, that would make it want to move in the opposite direction of the flow. But even then, the flow was strong enough to pull the protein through the nanopore. Maglia: ‘Previously, only easy to thread proteins were analysed. But we gave ourselves one of the most difficult proteins as a test. And it worked!
‘This proves that there is no fundamental limitation to sequencing proteins anymore,’ Maglia says. With his new startup called Portal Biotech, Maglia intends to make the nanopore technology from his lab available to users, such as labs and doctors. ‘With this latest research result, we have the missing piece that we needed to make protein sequencing happen.’
References
Giovanni Maglia. Electroosmotic flow across nanopores for single-molecule protein sequencing. Nature, 2023
Adina Sauciuc, Blasco Morozzo della Rocca, Matthijs Jonathan Tadema, Mauro Chinappi & Giovanni Maglia. Translocation of linearized full-length proteins through an engineered nanopore under opposing electrophoretic force. Nature biotechnology, 2023. 10.1038/s41587-023-01954-x
Previous news
| Last modified: | 10 February 2025 09.16 a.m. |
More news
-
25 April 2025
Leading microbiologist Arnold Driessen honoured
On 25 April 2025, Arnold Driessen (Horst, the Netherlands, 1958) received a Royal Decoration. Driessen is Professor of Molecular Microbiology and chair of the Molecular Microbiology research department of the Faculty of Science and Engineering at the...
-
24 April 2025
Highlighted papers April 2025
The antimalarial drug mefloquine could help treat genetic diseases such as cystic fibrosis, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, as well as some cancers.
-
22 April 2025
Microplastics and their effects on the human body
Professor of Respiratory Immunology Barbro Melgert has discovered how microplastics affect the lungs and can explain how to reduce our exposure.
