First image with Apertif: a new life for the Westerbork radio telescope
An important milestone for the Westerbork Synthesis Radio Telescope: the first images have been made using a revolutionary new type of receiver, called Apertif. Because of these new receivers, much larger areas of sky can be mapped in a single observation. The ‘old' Westerbork telescope could only map an area of sky comparable in size to that of the full moon in a single observation. The new Westerbork / Apertif system can image a region of sky 40 times larger, which is a great step forward. The new Apertif receivers, developed by ASTRON in Dwingeloo in cooperation with the Kapteyn Institute (University of Groningen), were installed on the Westerbork telescope over the last year and will be fully operational in the course of 2017.
With the upgraded Westerbork telescope there are numerous possibilities for new studies. In particular, Apertif will be used to make radio images of large areas of sky that have not been studied before and to search the sky for new and interesting types of galaxies and stars. In addition, compared with observations of single-dish telescopes, Apertif can map these large areas at much higher angular resolutions. This unique capability will be used to image large parts of the northern sky and provide a public database of images and catalogues that can be used for many astronomical projects done by astronomers from all over the world.
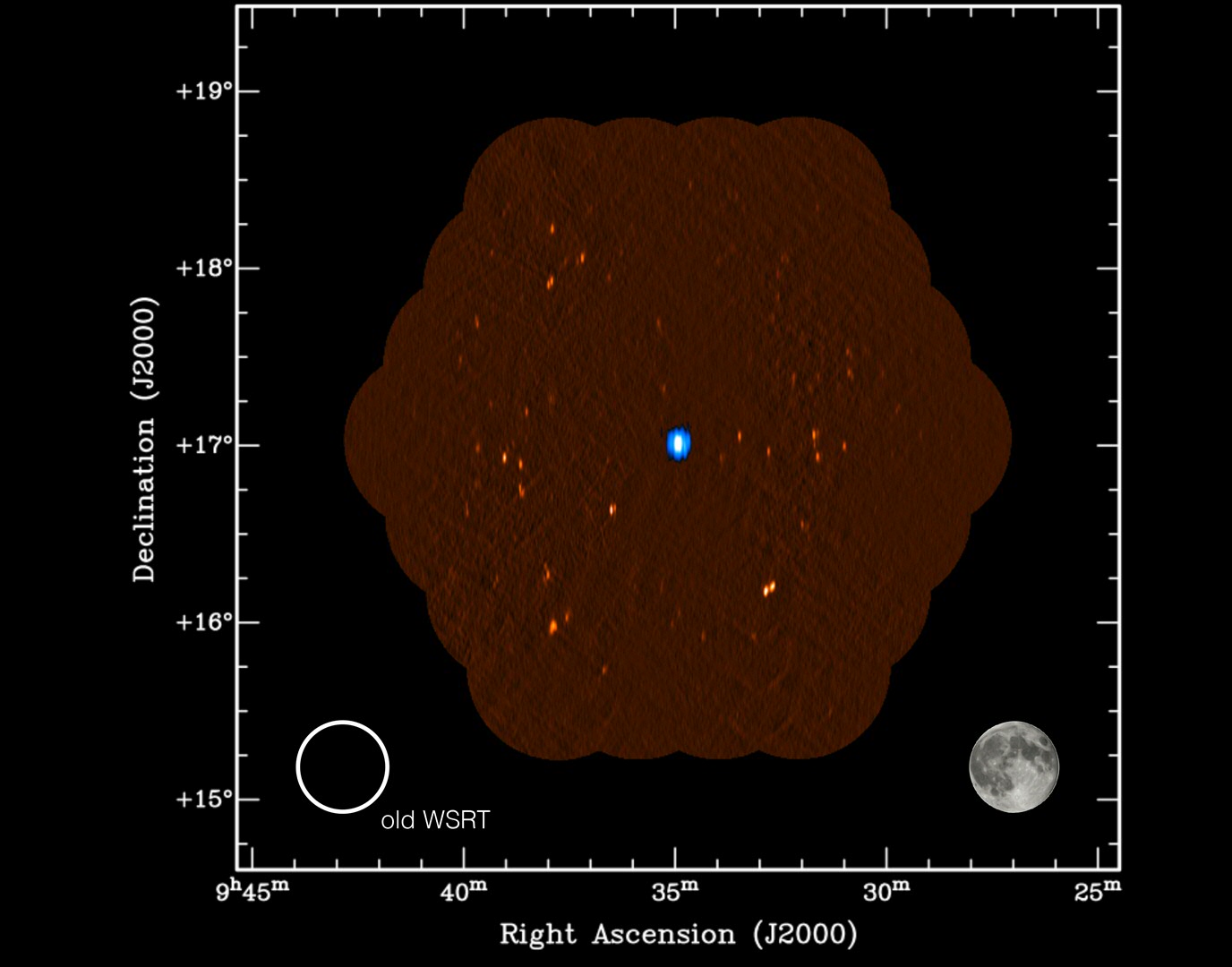
The first two radio images made with the upgraded telescope that demonstrate this new `wide-angle' capability are shown here. The first image shows the dwarf galaxy Leo T. The image is colour-coded and shows the gas (in blue) in this galaxy together with many distant radio galaxies in the background shown in orange. For comparison, the field of view of the previous Westerbork system and the size of the full moon are also indicated. "Leo T is a rare object and one of the smallest galaxies known. It is one of the big puzzles in astronomy how galaxies as small as Leo T can form and whether even smaller objects should exist. Apertif will be used to search the sky to see how many very small galaxies exist to help answer this question", says Prof. Tom Oosterloo from ASTRON, who is one of the principal investigators of the project.
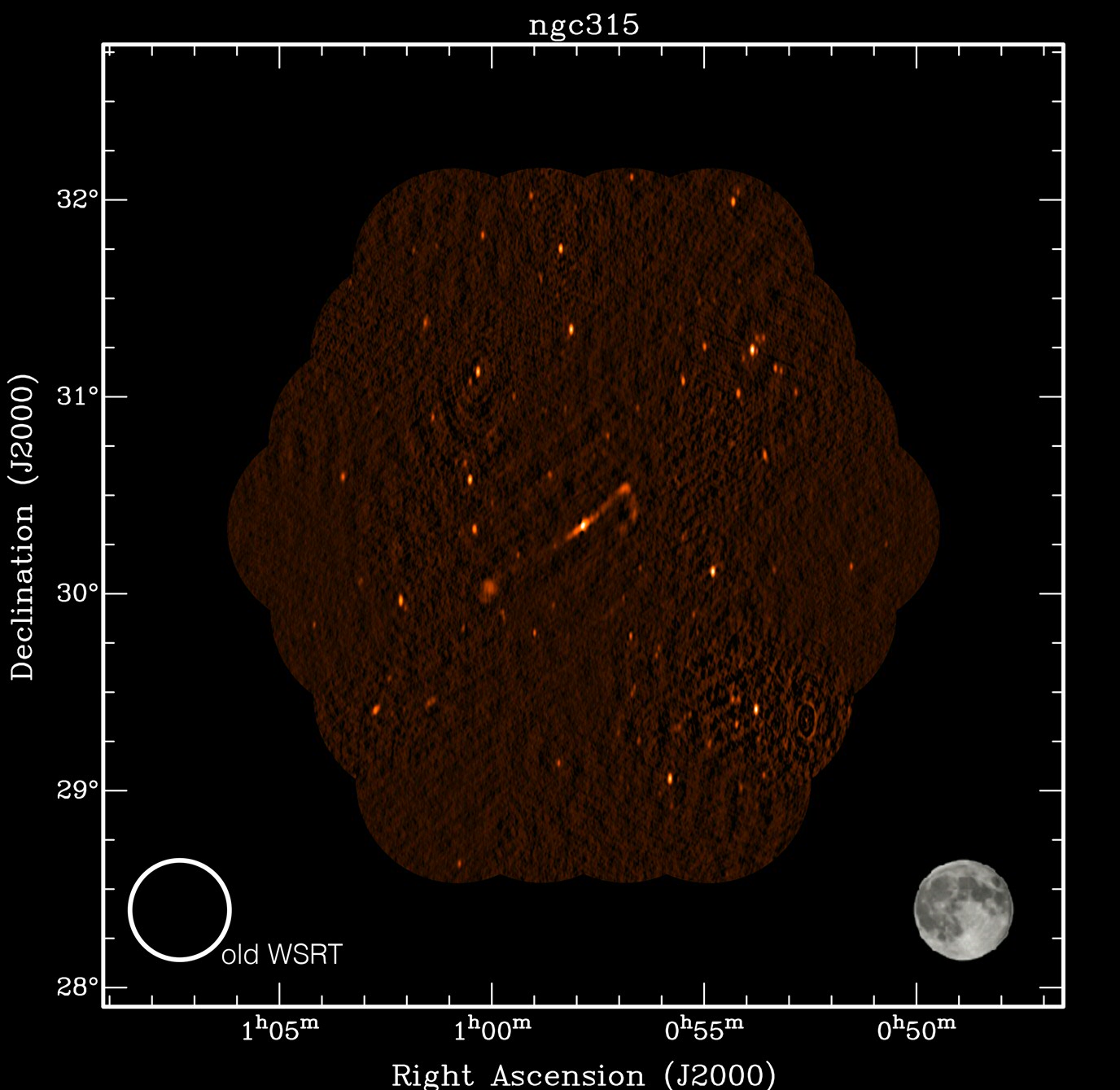
The second radio image shows the active galaxy NGC 315 with its extended jets and clouds of relativistic electrons that produce the radio waves captured by the Apertif receivers. "This image would have required almost 40 separate observations with the ‘old' Westerbork telescope while the new Apertif receivers can map this large galaxy in a single observation, demonstrating its `wide-angle' capability. Many such intriguing galaxies will be charted in detail with Apertif", according to Prof. Marc Verheijen of the Kapteyn Institute of the University of Groningen who is the other principal investigator of the project.
To make this new capability possible, ASTRON developed and built the hardware in-house. "We use 121 small receivers in each telescope whose signals are then combined electronically to produce the large field of view. The research and development that led to these new receivers are part of the contribution of ASTRON and the Netherlands towards the new technology that is needed for the next-generation international Square Kilometre Array telescope," says Ir. Raymond van den Brink, the Apertif Project Manager.
The upgraded telescope will also be used to search for and study new variable sources in the radio sky. With the new Apertif receivers, observations of large parts of the sky can be done much faster, and projects that used to be impossible as they would take tens of years can now be done in a much shorter time. Westerbork is therefore poised to make many new discoveries in the radio sky.
| Last modified: | 08 June 2017 1.32 p.m. |
More news
-
15 April 2025
1.5 million funding from Province of Groningen for innovative technology in the region
The University of Groningen will receive nearly 1.5 million euros in funding from the Province of Groningen to assist entrepreneurial academic researchers in developing innovative ideas into a startup.
-
15 April 2025
Nathalie Katsonis wins Ammodo Science Award 2025
For her pioneering research on molecular systems, Nathalie Katsonis receives the Ammodo Science Award for fundamental research 2025.
-
15 April 2025
Fundamental research with life-size effects
Nathalie Katsonis has won the Ammodo Science Award for Fundamental Research. She develops adaptive molecular materials and studies the chemical origins of life, which in turn yield insights for vaccines and clearing up oil spills at sea.
