Frequently Asked Questions

We receive daily questions from individual researchers and/or support staff working with or interested in research analytics. This FAQ aims to capture some of the most frequent or intriguing questions we have received and our attempt to provide an answer and guidance. If you cannot find the answer to your burning question below, don't hesitate to contact us.
Planning Impact
SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, Timely.
When planning the impact for your research, make sure your project and objectives meet those five goals.
|
What is SMART planning?
|
Example
|
||
|
S
|
Specific
|
Be as specific as possible when defining your impact goals. Ask yourself questions following the 5 W's: Who, What, When, Where and Why?
|
You are presenting your latest research at a scientific conference in Amsterdam, in a month. Your goal is to attract new collaborations with international peers in your field.
|
|
M
|
Measurable
|
Can you track your progress and measure your impact success? How? For tips, check out our page About measuring impact.
|
Before: you advertise your upcoming talk on social media and on your blog. Track altmetrics to assess your reach.
During: How many peers in your field attend the conference? How many attend your talk?
After: How many peers get in touch with you? Does your talk get shared on social media?
|
|
A
|
Achievable
|
The key to success is to set a goal that is just the right level of challenge to drive your progress: neither too easy nor too difficult to complete. Look at your current situation: do you have what you need to achieve your impact goal?
|
Do you have evidence that this method has helped you find collaborations in the past? Name all the resources that can help you reach your goal (social media, word-of-mouth, newsletters...) and use them.
|
|
R
|
Realistic
|
Is this impact goal worthwhile to you? Are you the right person to achieve it or should you delegate? Is it applicable to your current situation or unrealistic (see A - achievable)?
|
You realize you are not comfortable with using altmetrics to measure your success. You
contact the RISe team
to get appropriate support.
|
|
T
|
Timely
|
Assign a start and end date, possibly adding stepping stones in between, to ensure you are on track with your impact goal
|
You create a table with the important dates and corresponding goals to be achieved by then: before, during and after your talk.
|
Budgeting your research's impact is a crucial part of planning to ensure your research reaches and influences the intended audience effectively. Budgets vary depending on your activities, needs and fundings. Here, we provide general guidelines to help you get started.
Before anything else, make sure to define your research impact goals by identifying your target audience and outlining your impact objectives.
1. Plan your impact activities
-
Dissemination: Plan how you will share your research findings (e.g., academic publications, conferences, workshops, webinars, social media).
-
Engagement: Engage with stakeholders through focus groups, advisory boards, or collaborative projects.
-
Communication: Develop communication materials such as policy briefs, infographics, videos, and press releases.
2. Allocate resources accordingly
-
Personnel Costs: Budget for salaries, stipends, or consultancy fees for those involved in dissemination and engagement activities.
-
Event Costs: Include costs for organizing and attending conferences, workshops, and other engagement events (e.g., venue hire, travel, accommodation, catering).
-
Communication Costs: Consider expenses for designing and producing communication materials, maintaining a website, and utilizing social media platforms.
-
Monitoring Costs: Will you need to set aside a budget to track your impact? The UG's Research Intelligence Services are free to all university members, but if you decide to use metrics and tools other than those provided by us, you will need to take this into account in your research impact budget.
For more in-depth advice on budgeting and funding, contact the funding team.
Research collaborations can significantly enhance the quality, scope, and impact of scientific investigations. However, successful collaborations require careful planning, clear communication, and mutual respect. Follow RISe's twelve points for a successful research collaboration.
The Twelve Labours of Research Collaboration
-
Slay Ambuiguity - Establish Clear Objectives and Goals: Ensure a shared understanding of the research goals, objectives, and expected outcomes among all collaborators. Define how each collaborator’s expertise will contribute to achieving them.
-
Capture Responsibility - Define Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each team member to avoid duplication of effort and ensure comprehensive task coverage. Establish a leadership structure and decision-making processes. Designate a project leader or principal investigator.
-
Tame Uncertainty - Develop a Collaboration Agreement: Create a formal agreement that outlines the terms of the collaboration, including intellectual property rights, publication policies, data sharing, and conflict resolution. Specify how funding and resources will be shared and managed.
-
Purge Miscommunication - Communicate Effectively: Schedule regular meetings and use collaborative tools such as project management software, shared drives, and communication platforms to facilitate smooth and effective communication among team members.
-
Retrieve Information - Manage and Share Data Responsibly: Develop a data management plan addressing data collection, storage, sharing, and preservation, ensuring appropriate and secure access for all collaborators.
-
Inspire Trust - Foster Mutual Respect and Trust: Value and respect the expertise and contributions of all collaborators, building trust through transparency and reliability. Ensure consistent follow-through on commitments.
-
Protect Ownership - Clarify Intellectual Property and Authorship: Define intellectual property rights and authorship criteria early, following ethical guidelines and giving appropriate credit to all contributors.
-
Combat Conflict - Address Conflicts Constructively: Develop a conflict management plan and involve a neutral third party if necessary to mediate and resolve disputes.
-
Watch Progress - Monitor and Evaluate Progress Regularly: Regularly monitor the collaboration's progress against project goals and timelines, using defined metrics to evaluate success and output quality.
-
Harness Ethics - Uphold Ethical Standards: Conduct all research ethically, complying with relevant regulations and guidelines, and obtain informed consent from research participants when applicable.
-
Encourage Training - Provide Training and Capacity Building: Offer opportunities for skill development and knowledge sharing among team members to enhance overall collaboration.
-
Erect Perpetuity - Ensure Sustainability and Continuity: Plan for the long-term sustainability of the collaboration, identifying future project opportunities and maintaining comprehensive documentation for continuity.
Measuring Impact

Bibliometrics is the quantitative analysis of scientific output, scientific impact, or scientific collaboration. Information on these is provided through quantitative bibliometric indicators.
Bibliometrics analysis is used in research performance evaluation by a wide range of end-users – such as PhD candidates, researchers, research directors and administrators, as well as university policymakers – to build research profiles and identify important patterns and trends within their domains of interest.
Due to limitations associated with bibliometrics, these measures should always be used in conjunction with qualitative evidence such as peer review to ensure the most complete and accurate input in answering a question.
We can help you with creating research performance reports for the UG research community, for different levels of analysis. For help, please don’t hesitate to contact us.

The shift towards open access, the rise of web based and networked research and acknowledgment of the importance of societal impact of research have in recent years led to the development of alternative metrics. By capturing mentions in social media, blogs, news, policy documents, as well as the number of downloads, online readers and bookmarks, alternative metrics look beyond journal citations to give us more speedy and multifaceted feedback and a glimpse into how these impact broader audiences.
When used together with bibliometrics, altmetrics can provide a more holistic and broad picture of research and societal impact. This is not to say that it should be used without care – metrics in general, and in particular alternative metrics, should be transparent and reproducible in order to be used in evaluations. If in doubt, please contact us.

We use bibliometric and altmetric data to obtain a comprehensive understanding of research performance and impact. Several tools are available to conduct such analysis, and these are available to you too.
-
Scival - SciVal is an analytics tool offered by Elsevier that enables the visualization of research performance, benchmarking, analysis of collaborative partnerships and research trends. The data sources for Scival is Elsevier’s abstract and citation database of peer-reviewed literature called Scopus. While Scopus maintains that it is the largest such database, its coverage of certain disciplines is still limited
-
Altmetric - Altmetric tracks a range of online news and social media sources to capture and report on the attention surrounding scholarly output outside of academia.
Remember, these tools are available to everyone within the university of Groningen. Don’t hesitate to contact us for support with access and use!
The Field-Weighted Citation Impact is the ratio of the total citations actually received by an entity (researcher, research group, department, university, etc), and the total citations that would be expected based on the average of the subject field (see Scopus knowledgebase ). As such, it provides a "level playing field" for comparison as publications are compared to the average in their particular field, type and publication year.
However, when analyzing a larger publication set, simply calculating the average FWCI for this set can be very misleading especially when making a comparison between two such sets produced by two similar research groups. In cases like this, we recommend that you instead look at and plot the frequency distribution of the FWCIs of the publication set. For a clear example and more details, see "Profiles, not Metrics " paper published by the Web of Science Institute for Scientific Information (Jan, 2019).
When conducting bibliometric analysis, we often stress the importance of field-weighted indicators as these ensure fair comparison across document type, publication year and research area.
However, a blog post posted on the Bibliomagician platform recently exposed a subtle difference in Scival when computing field-weighted citation percentiles compared to the traditional bibliometric approach.
In a nutshell, instead of using total citation counts for each publication in the dataset under analysis, Scival uses citation ratios. Moreover, Scival merges subject areas before computing the top percentiles. As noted by the blog post authors, Scival’s method doesn’t lead to very different results for large datasets. However, it certainly affects the analysis for small datasets especially when that set includes publications from more subject areas, which have very different citation distributions.
We strongly encourage anyone using Scival to carefully read the whole blog post and send us any additional questions that may arise.
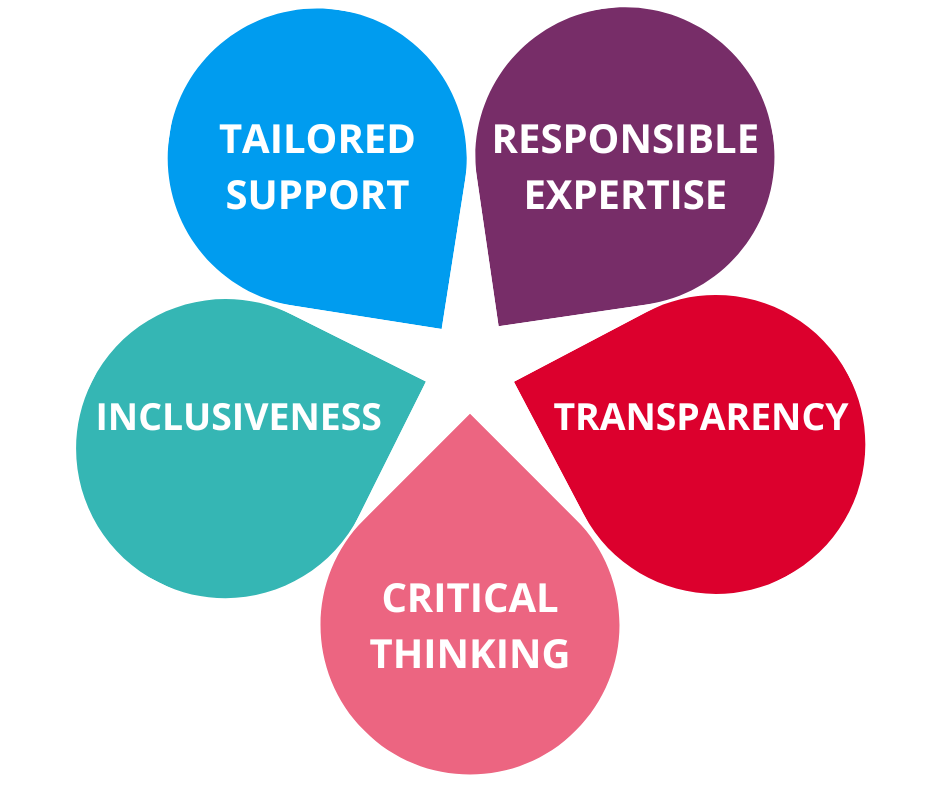
We strive to conduct our research intelligence analyses as ethically as possible, following our five core values:
-
Tailored support: we tailor our analyses to the mission of the research units.
-
Responsible expertise: we ensure the responsible and expert utilization of metrics across all practices at the UG.
-
Transparency: we openly share research assessment data and analyses.
-
Critical thinking: we thoughtfully select metrics that best serve their intended purposes and acknowledge their strengths and limitations.
-
Inclusiveness: we recognize the diverse nature of research disciplines and the varying research practices within them.
The University of Groningen recognizes the importance of using bibliometrics and altmetrics responsibly and adheres to the principles propagated in the Leiden Manifesto. The increasing sophistication of our benchmark tools allows us to do in-house analyses and provide benchmarks that can be used in various activities pertaining to research impact assessment, including SEP evaluations. As a result, the Research & Funding department of the Office of the University of Groningen has called for the prudent use of benchmarking tools and produced a set of Guidelines on this matter.
Disseminating Impact
Research findings and innovations come in many forms, and one way for it to have a societal or academic impact is by creating a research-based product. This can be an app, a software, a patented design, a start-up, etc. Such product can potentially be commercialized.
At RISe we do not provide support for such endeavour, but you can find facilitators here:
-
RUG Ventures (investment company)
-
Campus Groningen (incubator)
-
UMCG's Innovation Center (for health innovations)
-
Sustainable Startup Academy (course with practical tools)
That's a great way to disseminate your research! The University of Cambridge has put together a quick-guide on how to get started.
| Last modified: | 22 July 2024 12.56 p.m. |

